Have you ever wondered how does a garage door opener works? How a simple push of a button effortlessly glides your garage door open? Behind this seemingly simple operation lies an intricate system that combines mechanics with technology.
Understanding how a garage opener works is often the difference between making the right and wrong choice while buying one.

The mechanics of different types of garage openers vary, and thus, their applications are also different. While they have (more or less) the same components, their arrangement and how they function together make a difference.
In this guide, we will offer an in-depth explanation of how a garage opener works. We’ll also discuss the different types of garage openers and how these mechanisms impact their applications.
So, let’s get on with it.
Connect With A Garage Expert
Connect with local experts, Compare quotes, Get the best price.
How Does a Garage Door Opener Work?
A garage door opener receives an activation signal from a remote control, smartphone application, or a button inside a keypad hardwired directly to the motor. This signal activates the electric motor (inside the opener), which slides the door up or down its tracks using different types of opener driver mechanisms (i.e., belt, chain, or screw).
There are several components inside a garage door opener. Some of the components are fundamental and available in all garage openers, while others are add-ons that improve convenience or safety.
Let’s discuss the fundamental components of a garage door opener in detail to understand how it works.
Garage Door Opener Motor
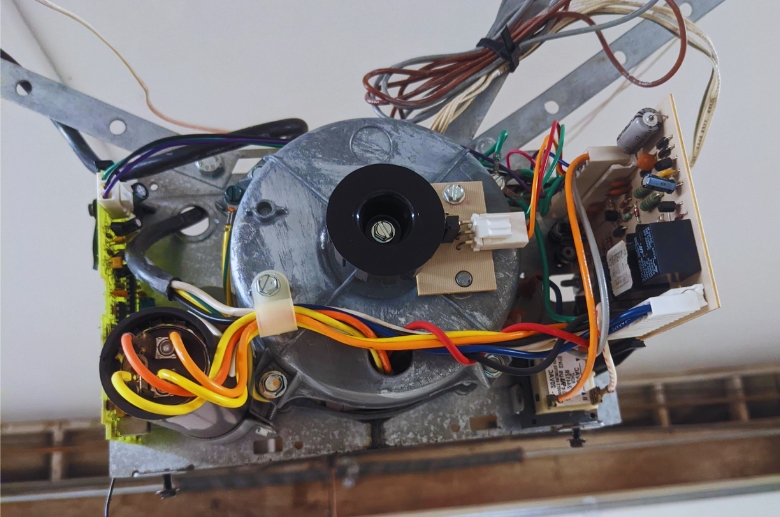
The motor is the key component of a garage opener. It provides the power to open and close the door. The motor activates upon receiving a signal from a wireless device such as a remote control or smartphone. You can also activate the motor by pushing a button on the hardwired keypad.
Upon activation, an electric current flows through the wiring in the electric motor. The motor uses the electrical energy from the wiring to power the drive mechanism, such as chain, belt, or screws.
Types of Garage Opener Motor
Depending upon the type of garage opener, the motor is either AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current).
DC motors offer quieter operations, making them suitable for residential garages. Some DC motors also come with battery backups, meaning they can open the door even when the power is out. These motors are energy efficient and ensure a smooth operation. In residential settings, a key consideration is choosing between a belt vs chain garage door opener, each offering distinct advantages in terms of noise level and durability.
AC motors, on the other hand, offer more power. They have been used in the industry for longer, are cheaper, and more reliable than DC motors. However, they are louder and larger than DC motors, therefore, AC motors are more suitable in commercial or industrial settings where power is the priority.
Garage Door Opener Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit that represents the power of a motor. In simple words, a motor with a higher horsepower is more powerful (can lift more weight) than one with a lower horsepower.
So, when choosing a garage door opener for your garage door, you should look for one with enough horsepower to lift the weight of your door easily. Choosing an opener with insufficient horsepower will cause strain and lead to premature failure. On the other hand, choosing one with more horsepower than required is an unnecessary expense.
The following table provides a list of garage door motors with different horsepower and how much weight (estimated) they are capable of lifting without premature failure:
| Garage Door Motors | Garage Door Weights |
| ⅓ hp | Garage doors weighing 350 lbs. |
| ½ hp | Garage doors weighing 350 lbs. |
| ¾ hp | Garage doors weighing 600 lbs. |
| 1 hp | Garage doors weighing 750 lbs. |
| 1 hp+ | Garage doors weighing 750+ lbs. |
If you don’t know how much your garage door weighs, don’t worry. Since we know the weights of standard garage doors, we can suggest how much horsepower you’ll need.
A ⅓ hp garage door opener:
It’s an uncommon option and is usually suitable only for lightweight garage doors. These openers are used for one-car garage doors (10 feet by 8 feet). But these openers are not efficient or durable compared to ½ hp openers.
A ½ hp garage door opener is sufficient for:
- Standard steel garage doors (8 feet by 7 feet)
- Standard double-car garage doors (16 feet by 7 feet)
- Single-layered Wooden garage doors (8 feet by 7 feet)
A ¾ hp garage door opener (or higher) is needed for:
- Oversized steel doors that are over 14 feet in width require a 3/4 hp
- Double-layered wooden door (custom-made)
If you’re unsure of what garage door opener to buy, it is better to get one that might be overkill than one that might be underpowered. Better yet, consult a garage door expert to
The Trolley and Rail System
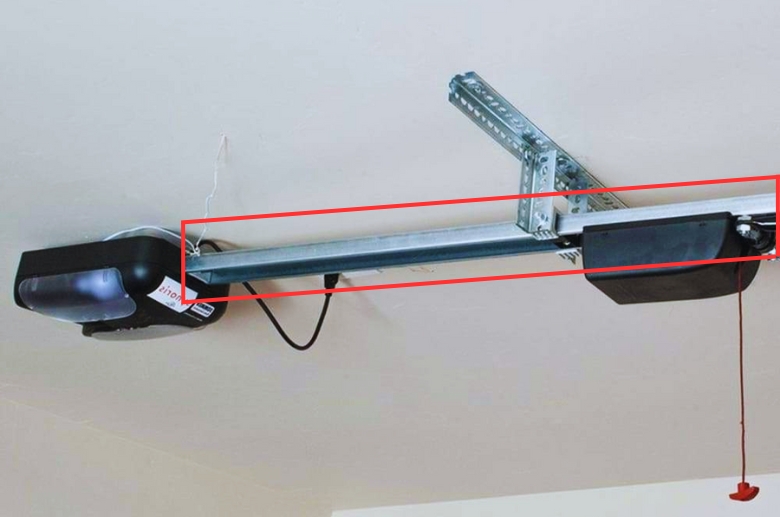
The trolley and rail system opens and closes garage doors by gliding them on a designated path. As the name implies, it uses two components: a trolley and a rail.
Trolley
At one end, the trolley connects with the garage door, allowing it to move upwards and downwards. On the other end, it connects with the driving operator (e.g., chain, screw, or belt), which drives the trolley along the rail.
The type of driving operator determines the type of garage door opener and its applications. Chain drives are most common in heavier doors, such as wooden or insulated garage doors, because strong metal links can lift heavier weights.
Belt drives, on the other hand, are used for both multi-panel and single-panel garage doors. They can lift both light and heavy doors, making them more diverse.
Rail
A rail is a long and rigid track mounted horizontally along the ceiling of a garage. It guides the movement of the trolley, ensuring it remains in a straight line. As the trolley moves through the rail, it either opens or closes the door, depending on its movement.
Safety Mechanisms
Modern garage door openers offer a range of safety mechanisms, including auto-reverse and manual release mechanisms and rolling code technology; the most popular of them include;
Photoelectric Safety Sensors
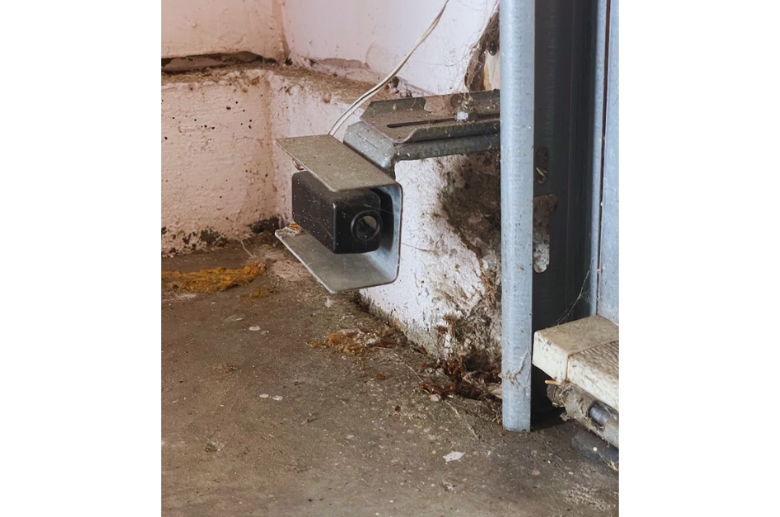

Photoelectric sensors are near the bottom, at both sides of the door’s track. They emit a beam of light, so any obstruction in their path will break the connection between the two sensors. As soon as the obstruction breaks the beam signal, the garage door operation immediately halts or reverses.
So, if your pet, child, or vehicle is standing below the garage door as it closes, the beam signal breaks and prevents the door from closing. Photoelectric garage door sensors, therefore, prevent accidents and serious injuries.
That is why, according to U.S. federal law UL 325, all garage doors must have safety sensors (or other safety mechanisms).
Force Setting
Force setting allows the homeowner to set the maximum force a garage opener will exert when closing. It prevents accidents because the moment the door detects resistance from the vehicle, pet, or kid, it shuts its operations or starts reversing. You can configure the amount of force to detect even small obstructions, such as a cat.
Connect With A Garage Expert
Connect with local experts, Compare quotes, Get the best price.
Control Mechanisms
The control mechanism involves a combination of switches, electrical circuits, and remote communication to operate a garage opener. The common types of control mechanisms include;
Wall Switches
Wall switches are mounted inside the garage. A button push signals the motor to lower or lift the garage door. The wall switches can also be mounted outside the garage with a wireless keypad. Homeowners must enter a specific code to open or close the door from outside to prevent intrusion.
Remote Control
Some control mechanisms use a combination of a receiver and a wireless device to activate the garage motor, often called wireless garage door openers.
As you press the button from the remote control, the receiver detects it and sends activation signals to the motor, which either lifts or lowers the garage door.
Modern smart garage door openers also use Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing homeowners to close and open the door from their smartphones.
Emergency Release Cord

An emergency release cord is a safety and security feature that allows homeowners to manually operate garage doors during malfunctions or when the power goes out.
Typically, the release cord is available near the motor unit, mounted on the garage trolley. It features a rope with a handle or knob at the end. Upon releasing the emergency cord, it disengages the trolley of the door opener, allowing you to move the door along the rail manually.
Note: Using an emergency release cord cautiously is important because once you engage it, the safety and security mechanisms become redundant. So, it will not detect obstruction in its path, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
Security Enhancements
Modern garage door openers offer sophisticated security enhancement to prevent burglary and damage to the property. Rolling codes and integration with home security systems are the two commonly used security add-ons.
Rolling Code
Rolling code technology generates new code with every use available to homeowners only. The uniqueness of the code prevents thieves from replicating it, preventing unwanted access even if they replay the remote signal.
Integration With Home Security
A home security integration system is a more sophisticated option, which detects unidentifiable movement and alerts the homeowners. It helps keep track of the door’s opening and closing from your smartphone.
Additional Accessories
You can use a range of accessories while installing garage door openers to make them more effective and secure, which include;
- The timer-to-close module lets you close the garage door automatically after a certain time.
- Light control allows you to control the lights remotely to reduce accidents while parking the vehicle and getting out in the dark.
- Motion Sensors detect the movement of the garage door openers to trigger the lights on. A sophisticated form of these sensors also sends alerts to the smartphone if they detect any usual movement outside or inside the garage.
- Battery backup allows you to operate a garage door opener even when the power is out.
- Security Cameras offer real-time footage of what is happening around the garage. You can also configure them to send alerts if they detect unusual movement for an added layer of security.
- External Emergency Release Lock allows homeowners to operate the garage door opener when the power is out from the outside. Typically, it comes with a key, which, when inserted, opens the door.
Types of Garage Door Openers
The drive mechanism serves as an overlay between the motor and the garage door and uses the power from the motor to open or close the door.
Let’s discuss the four most popular drive mechanisms and their applications below.
Belt Drive Opener
Average Cost: $225 to $500
As the name implies, belt-driven garage door openers use a rubber belt to move the trolley. The lack of metal reduces vibrations, making it the quietest of all mechanisms. Their simpler operation also makes them easy to maintain but at higher costs.
Chain Drive Opener
Average Cost: $175 to $350
Chain operators are the most economical garage door openers. The trolly moves along a metal chain to open and close the door, which produces a lot of noise. Such systems are usually used for heavier doors and are ideal for houses that have garages detached from the living areas.
Screw Drive Opener
Average Cost: $190 to $350
A screw drive opener uses a threaded steel rod. As the rod rotates, it moves the trolley, which opens and closes the garage door.
Screw drive openers are not as popular as chain drive or belt drive openers, but they offer a much smoother and quieter operation because of fewer moving parts. They also require less maintenance. You just need to lubricate the screw rod biannually.
However, screw drive openers are not great for heavier doors and break down if the temperature fluctuates drastically, making them viable only in specific climates.
Jackshaft
Average Cost: $600 to $1,000
Jackshaft garage door openers have a completely different design. Instead of the traditional trolley and rail system, they use a network of cables and pulleys.
As you activate the motor, it begins to tighten the cables with the movement of pulleys to lift the door and release the tension to close it. The operation of jackshaft garage doors is quieter and costs less. Since jackshaft openers don’t require a lot of ceiling space, they’re great for low-headroom garages.
Final Thoughts
Garage door openers are a fascinating blend of mechanics and technology. Understanding these components helps in selecting the right garage door opener for you and also comes in handy when fixing garage door openers.
Understanding how a garage opener works also helps in finding suitable accessories that make the operations smoother and more secure.




